Positives

- No delay
- Almost no increased cost
- Goodput stays unchanged
- Jostling very low
- Good Scope
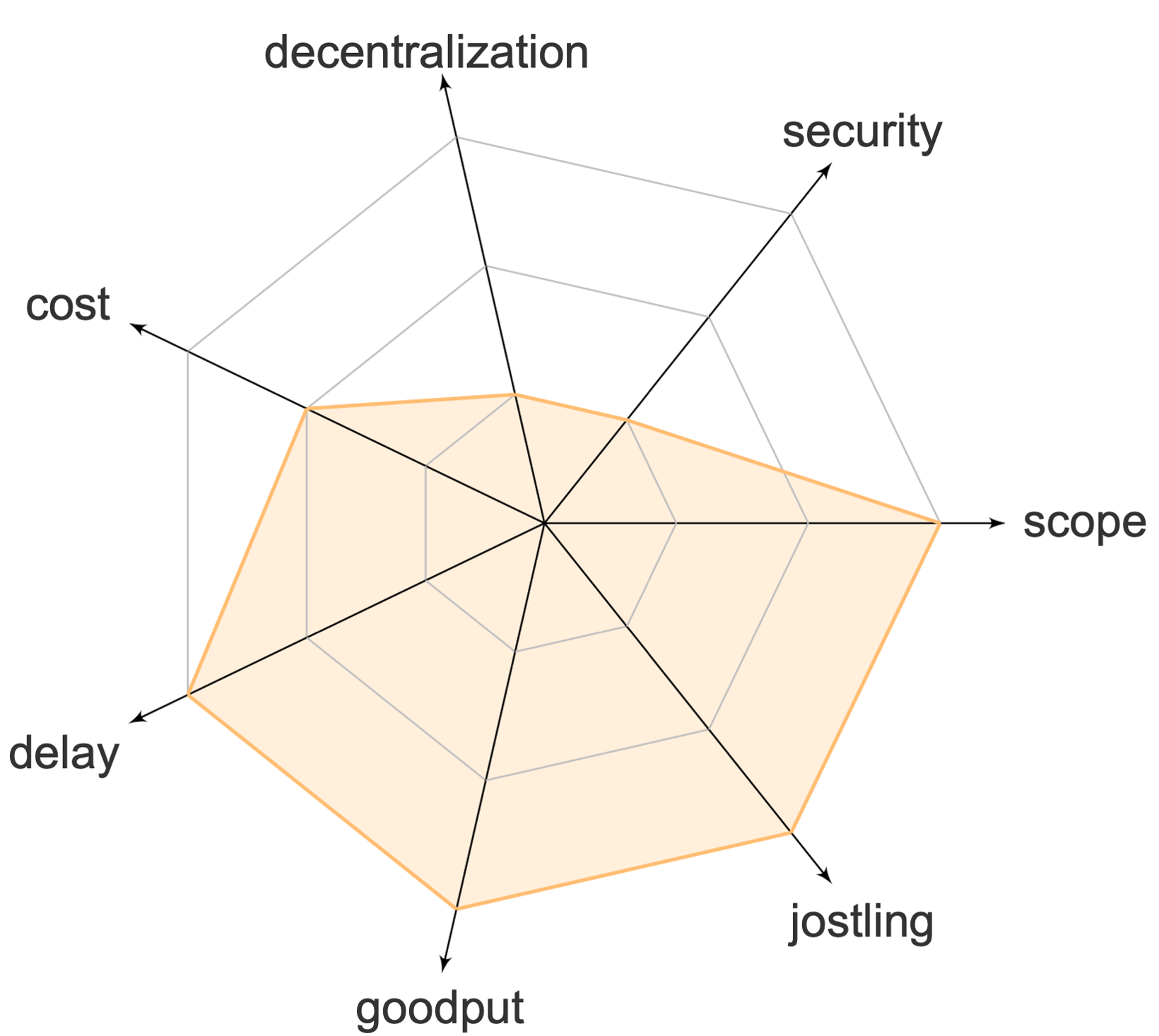
Negatives
- Decentralization impacted
- Security in case of byzantine third party
Trusted third party ordering refers to schemes that entrust a trusted third party with the ordering. Transactions are sent directly to the trusted third party who then orders them. Thus, these schemes order transactions efficiently while compromising decentralization and security.






This page is mantained by the Distributed Computing group at ETH Zürich. We are not liable for any false information.
Copyright © 2024 Distributed Computing Group, ETH Zürich