Positives

- Good Scope
- Minimal Jostling
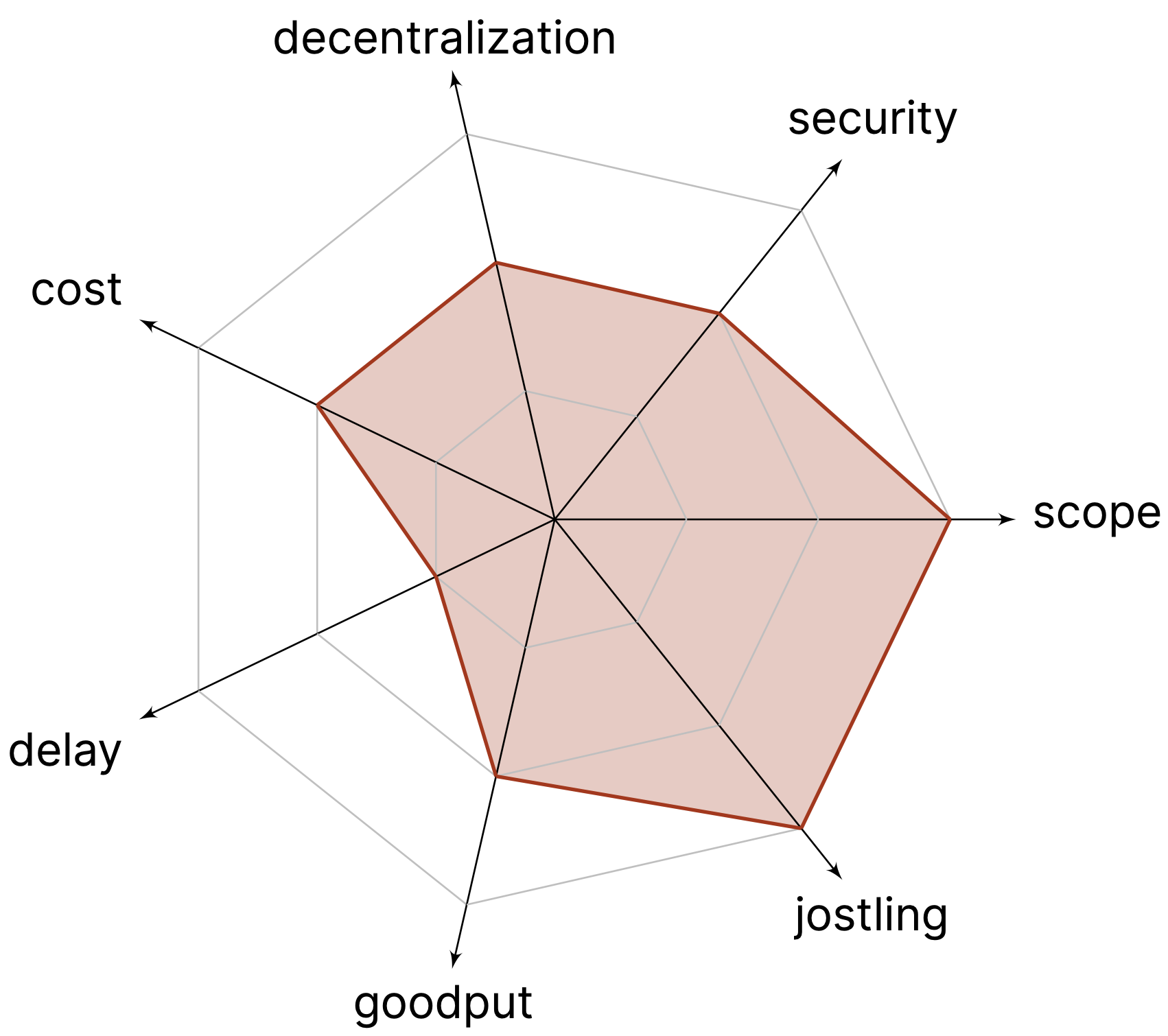
Negatives
- Increased cost
- Increased delay
- Reduced decentralization
- Security in case of byzantine committee
Randomized ordering protocols gather transactions over a set period and then execute them in a random order to prevent front-running on the blockchain. This approach ensures unpredictability and fairness in transaction processing but may not be ideal for time-sensitive trades.






This page is mantained by the Distributed Computing group at ETH Zürich. We are not liable for any false information.
Copyright © 2024 Distributed Computing Group, ETH Zürich